Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) Software
Maintenance – a cost factor or a success factor?
The importance of maintenance is often not properly assessed. The focus is often primarily on the costs of maintenance – but maintenance is more than that, it is a strategic success factor. Around half of production costs are directly or indirectly influenced by successful maintenance management. Improvements in reliability and performance as well as stability of the production process are the results that can be achieved here.
With the Legato Sapient TPM software from Germanedge, you have the perfect tool in your hand to optimize your maintenance and increase efficiency in your company, because you can keep your downtimes to a minimum and demonstrably reduce costs.
Advantages of our Total Productive Maintenance software
Functions of our TPM software
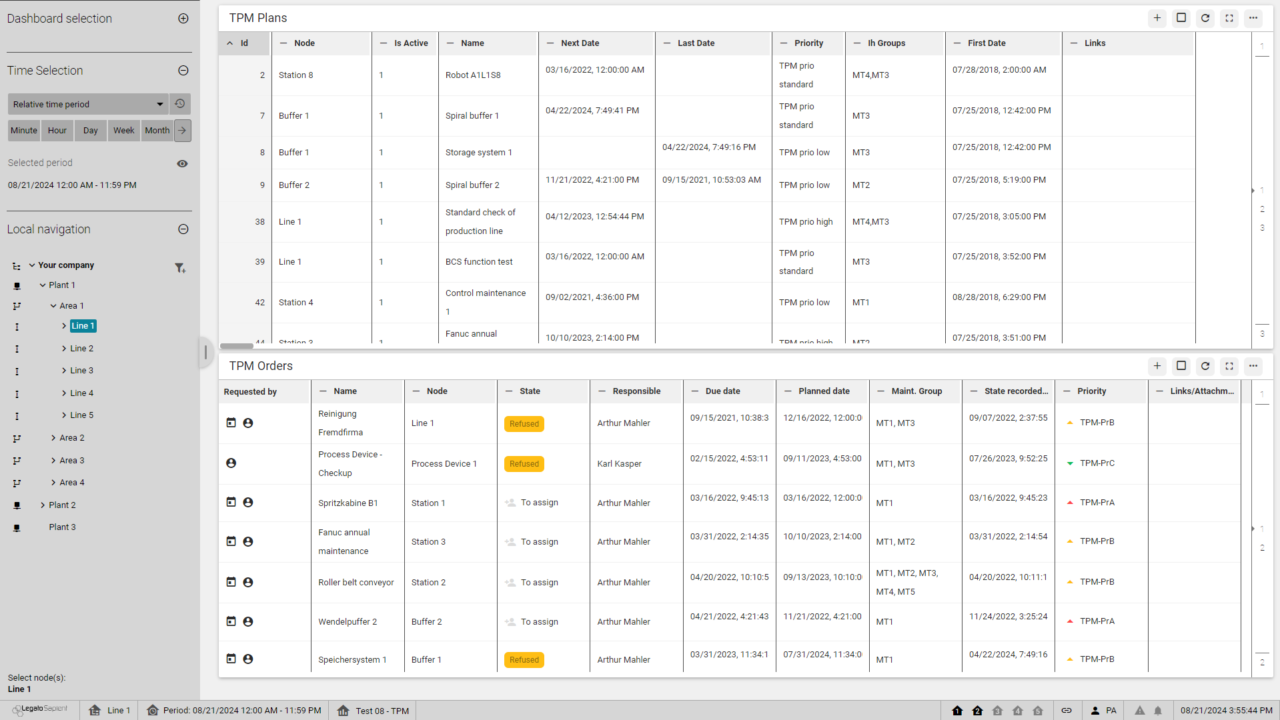
Our TPM is used for the central management and implementation of all maintenance processes across all areas (Shopfloor, Facility Management, etc.). We would like to explain the most important functions in more detail below.
Administration all activities in maintenance
Germanedge’s TMP system ensures that you can organize and efficiently manage all maintenance activities (such as material, personnel, time, duration, activities). You can schedule the various maintenance times required, taking into account the production situation (delivery reliability, alternative resources, synchronized maintenance within an area).
It is also possible to list all maintenance activities for a maintenance order and coordinate their execution.
Planning of all maintenance/inspection cycles
Our maintenance software helps you to ensure flawless operation in your company on the basis of supplier specifications. By knowing the best possible maintenance time (condition-based maintenance) and the activities to be carried out (maintenance duration), it is possible to make a precise statement about the time and duration of maintenance for a resource. This helps when scheduling production orders in order to avoid conflicts caused by unavailable resources and to maintain production using alternative resources.
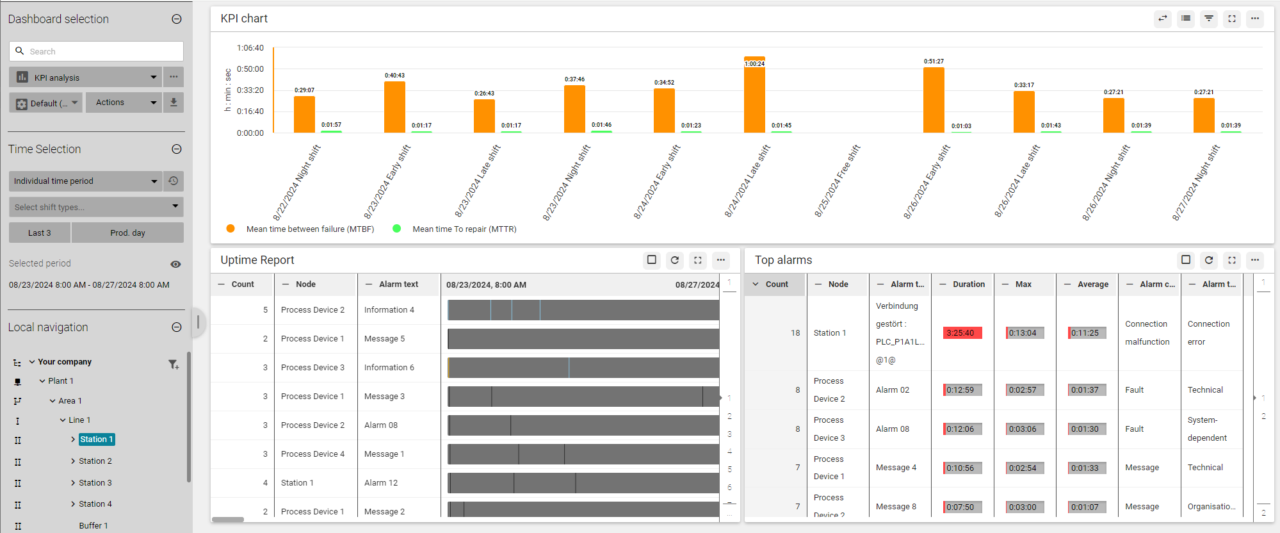
Evaluation of data for further forecasts
You can use the TPM software to evaluate current and historical data, such as reasons for faults or specific events. This analysis enables you to make predictions about wear and tear or machine downtime in order to prevent malfunctions. This allows your production to run more smoothly. Real-time monitoring of systems also supports the maintenance process. This means that the maintenance technician is also actively notified of unscheduled maintenance (unplanned maintenance and repairs in the event of sudden malfunctions) in order to shorten response times and thus reduce downtimes.
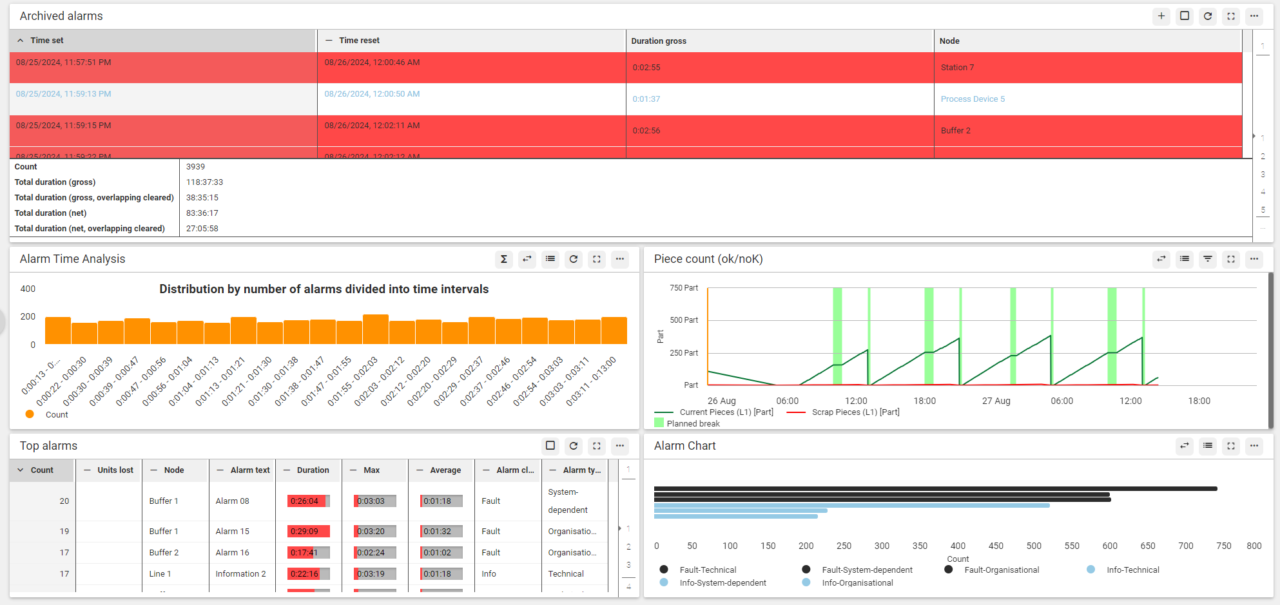
Recording and archiving of all maintenance information
The recording and archiving of all maintenance information serves, among other things, as proof of compliance with the system supplier’s maintenance regulations (warranty) and as a basis for the continuous improvement process (CIP).
All documents relevant to maintenance are linked to a maintenance plan and are therefore automatically available to the maintenance personnel when the maintenance order is carried out.
Integration of the workforce scheduling software
Step-by-step instructions for integrating the TPM software at your company:
- Contact us
- We show you the solution in a live demo
- We discuss the requirements and technical integration with you
- We support you with the integration and onboarding
Book your demo appointment now.
In general, the TPM solution can also be launched without a machine connection. In this case, the maintenance orders can only be triggered via time intervals
- The real added value is then only achieved in conjunction with the recording of actual data from the system controls (process values, machine status, etc.).
- On the one hand, to offer maintenance additional options via visualization and monitoring (alarm management, key figures, etc.).
- On the other hand, to trigger maintenance orders based on maintenance-relevant criteria – with online data from the shopfloor.
FAQ: Frequently asked questions about the TPM software
What does TPM stand for?
TPM stands for Total Productive Maintenance.
What is TPM?
TPM (Total Productive Maintenance) is a comprehensive production and maintenance system that aims to maximize the efficiency of machines and systems, minimize downtime and improve product quality. TPM integrates maintenance into the daily production process and promotes cooperation between the various departments of a company. It is based on preventive and predictive maintenance in which all employees are actively involved in order to achieve continuous improvement of production processes.
What effects does the use of TPM have on the company?
The use of TPM can lead to the following positive effects in a company:
- Increase machine availability: regular maintenance and preventive measures minimize unplanned downtime.
- Improving product quality: A precise and well-maintained machine reduces production errors.
- Increase employee involvement: TPM promotes a culture of continuous improvement in which all employees actively contribute to optimizing processes.
- Reducing costs: Reducing machine breakdowns, rejects and rework reduces production costs.
- Extending the service life of systems: Regular maintenance and care of machines leads to a longer service life and lower replacement costs.
How can a company benefit from TPM?
A company can benefit from TPM by:
- Maximizing machine and equipment availability, resulting in higher production capacity and better delivery performance.
- Reducing maintenance and repair costs, as planned and preventive maintenance is more cost-effective than unplanned repairs.
- Product quality improved, resulting in a lower error rate and fewer rejects.
- Workplace safety is increased, as machines and systems can be operated more safely through regular maintenance.
- Employee motivation increases as they take responsibility and contribute to continuous improvement through their active involvement in maintenance.
What are the advantages of TPM?
The advantages of TPM are
- Reduced downtime through preventive maintenance.
- Improved machine performance and higher efficiency.
- Increased product quality through optimized and stable production.
- Cost savings through a reduction in breakdowns, repairs and rejects.
- Increased safety in the workplace through well-maintained machines.
- Strengthened teamwork and cross-departmental cooperation.
- Continuous improvement of production processes through systematic fault analysis and elimination.
What are the goals of TPM?
The main objectives of TPM are
- Maximizing plant efficiency by minimizing downtime and production losses.
- Reducing machine malfunctions through preventive and predictive maintenance.
- Improving production quality through stable and error-free processes.
- Increasing occupational safety through well-maintained machines and a safe working environment.
- Promoting a company-wide culture of continuous improvement and active employee participation.
- Extending the service life of machines and systems through regular care and maintenance.
What are the pillars of TPM?
TPM is based on eight pillars, which are regarded as the cornerstones for implementing the system:
- Autonomous maintenance (Jishu Hozen): Training operators to perform simple maintenance tasks autonomously.
- Planned maintenance: development of a preventive maintenance plan to avoid machine breakdowns.
- Quality maintenance: Focus on preventing defects through continuous monitoring and improvement of production processes.
- Efficient plant management: Measures to increase the efficiency of machines and plants.
- Education and training: Training employees to improve their maintenance skills.
- Occupational safety and environmental protection: Promotion of a safe and environmentally friendly working environment.
- Early integration of maintenance: Consideration of maintenance requirements as early as the planning and development phase of new machines and systems.
- Office TPM (Administrative TPM): Application of TPM principles to administrative and support processes in the company.
What are the requirements for TPM?
TPM is based on the following prerequisites:
- Management support: The management level must actively support the TPM system and provide the necessary resources.
- Involvement of all employees: TPM requires the active participation of all employees, not just maintenance staff.
- Regular training: Employees must be regularly trained to implement the principles and techniques of TPM.
- Transparent communication: Open and clear communication is crucial to achieve the goals of TPM and coordinate improvements.
- Data-based decision making: Use data to monitor plant performance and identify opportunities for improvement
What does OEE have to do with TPM?
OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) is a key performance indicator that is often used in connection with TPM. OEE measures the efficiency of a machine or system based on three factors: availability, performance and quality. TPM aims to maximize OEE through preventive maintenance, training and continuous improvement measures. Through TPM, companies can identify the causes of inefficiencies and take action to increase OEE, which in turn leads to better utilization of production capacity and higher profitability.
The ability to automatically record production data (machine downtimes, process parameters, etc.) provides high-quality data in near real time. In addition to the important production indicator OEE, there are other key performance indicators specifically for maintenance to assess production efficiency – such as
- MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures): Mean operating time between failures for repairable units
- MTTR (Mean Time To Repair): Mean repair time after a system failure
Get in touch!
Would you like to know more about our solutions? Then please write us using the contact form. My colleagues and I look forward to exchanging ideas with you.

Dominik Weggler
Head of Sales Germanedge